
The appropriate education and skills are critical for success and career advancement in today’s cutthroat business environment. The best business courses you take can greatly impact your ability to succeed, whether you are an aspiring entrepreneur, a future business leader, or just looking to improve your current business knowledge. Many options are available in business education, ranging from undergraduate programs to specialized certifications and advanced degrees.
This article aims to help you choose the best courses to study for business by providing information on the different academic specialties, employment prospects, and advantages of enrolling in these programs. So let us explore the best courses for business professionals if you are prepared to realize your potential and lay the foundation for a successful career in the corporate world.
What Is A Business Degree?
Studying business is an academic path that prepares students for careers in the business world. This includes various subjects like finance, marketing, management, entrepreneurship, economics, accounting, human resources, and operations. Different levels of business degrees are available, such as undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral programs. Students will learn fundamental business theories, concepts, and practices and develop skills in leadership, communication, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
The Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) is the most popular undergraduate degree, while the Master of Business Administration (MBA) is a common choice at the graduate level. The curriculum for a business degree typically combines core courses with electives that allow students to focus on specific areas of interest.
With a business degree, graduates can pursue careers across various sectors and industries, including corporations, governmental organizations, non-profits, consulting firms, and startups. Job positions include financial analyst, marketing manager, human resources specialist, operations manager, project manager, or business owner.
Top 25 Courses To Study For Business 2023
Let us look at a few courses to study for business;
1. Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA)

Many aspiring business professionals opt for a Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) degree. This thorough undergraduate degree offers a strong foundation in several business fields, including marketing, management, finance, and entrepreneurship. Students study actual case studies, work on group projects, and hone their critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Graduates with a BBA are prepared to enter various industries and pursue various career paths.
The Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) is a popular undergraduate degree program that provides students with a comprehensive understanding of various aspects of business and management. The specific subjects and curriculum may vary slightly from one university or college to another, but generally, a BBA program includes a mix of core business subjects and elective courses.
Here are some common subjects that are typically covered in a BBA program:
- Principles of Management
- Business Communication
- Financial Accounting
- Managerial Accounting
- Business Statistics
- Marketing Management
- Human Resource Management
- Operations Management
- Business Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility
- Organizational Behavior
- Business Law
- Economics for Managers
- Financial Management
- Strategic Management
- Entrepreneurship
- International Business
- Information Technology for Business
- Business Research Methods
- Consumer Behavior
- Supply Chain Management
- Risk Management
- E-commerce
- Business Analytics
- Leadership and Team Management
- Project Management
Apart from these core subjects, BBA programs often offer students the flexibility to choose elective courses based on their interests and career goals. These electives can cover a wide range of areas, including finance, marketing, human resources, international business, information technology, and more.
Keep in mind that the availability and specific subjects offered may vary depending on the university or college you choose. It’s essential to check the curriculum of the particular institution you are interested in to get a detailed list of subjects.
2. Master of Business Administration (MBA)

The MBA is the pinnacle of business education and is highly regarded by employers worldwide. An MBA program provides a deeper and more comprehensive understanding of leadership, strategic management, and decision-making.
It improves students’ analytical and critical thinking abilities and positions them for management and executive positions. With an MBA, people can gain a competitive edge and open up higher-level career opportunities across industries.
The Master of Business Administration (MBA) is a graduate-level degree program that provides students with advanced knowledge and skills in various areas of business and management. MBA programs are designed to prepare individuals for leadership roles in business and are highly versatile, offering a wide range of subjects to cater to different career paths and interests. While the specific subjects may vary depending on the business school and specialization chosen, here are some common MBA subjects:
- Financial Accounting and Reporting
- Managerial Accounting
- Corporate Finance
- Marketing Management
- Operations Management
- Human Resource Management
- Organizational Behavior
- Business Ethics and Corporate Governance
- Strategic Management
- Managerial Economics
- Business Statistics and Data Analysis
- Leadership and Team Management
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation
- Global Business and International Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Business Law and Ethics
- Managerial Communication and Negotiation
- Business Research Methods
- Information Technology and Business
- Managerial Decision Making
- Project Management
- Risk Management
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Business Analytics and Big Data
- Marketing Strategy and Brand Management
Apart from these core subjects, many MBA programs offer specialization tracks or concentrations that allow students to focus on specific areas of interest, such as finance, marketing, entrepreneurship, healthcare management, information technology, and more. The elective courses in these specializations further enhance the students’ expertise in their chosen field.
It’s important to note that the subjects offered in an MBA program can vary from one business school to another. Additionally, some MBA programs also include experiential learning components, such as internships, consulting projects, or study abroad opportunities, to provide practical exposure and real-world experience to students. As you consider pursuing an MBA, I recommend researching specific business schools and their respective MBA curricula to find the one that aligns best with your career goals and interests.
3. Finance

Management and allocation of financial resources are the main areas of finance in business. Various subjects are included in finance courses, such as financial analysis, investment management, corporate finance, and risk management. Individuals who pursue careers in banking, investment firms, corporate finance, and financial consulting benefit from a solid understanding of financial planning, valuation, and decision-making.
Finance is a specialized field within business and economics that deals with the management of money, investments, and financial assets. In finance-related programs, whether as part of a Bachelor’s, Master’s, or MBA degree, you can expect to encounter a variety of subjects that cover different aspects of financial theory, analysis, and practice.
Here are some common finance subjects that you might encounter in your academic journey:
- Financial Accounting
- Managerial Accounting
- Corporate Finance
- Investment Analysis and Portfolio Management
- Financial Statement Analysis
- Financial Markets and Institutions
- Risk Management and Insurance
- Derivatives and Financial Engineering
- Fixed Income Securities
- Equity Valuation and Analysis
- International Finance
- Behavioral Finance
- Mergers and Acquisitions
- Financial Modeling
- Private Equity and Venture Capital
- Corporate Restructuring
- Capital Budgeting
- Financial Planning and Wealth Management
- Real Estate Finance
- Treasury Management
- Financial Regulation and Compliance
- Quantitative Finance
- Islamic Finance (in certain regions with interest in Islamic banking)
- FinTech and the Future of Finance
- Ethical Issues in Finance
Keep in mind that the exact list of finance subjects may vary based on the program level (undergraduate vs. graduate) and the specific focus of the finance curriculum. Additionally, if you pursue a degree in finance, you might have the opportunity to choose elective courses that align with your interests or career goals, allowing you to explore specific areas in greater depth.
Whether you aim to become a financial analyst, investment banker, financial planner, or work in any other finance-related role, a strong understanding of these subjects will provide you with a solid foundation for success in the finance industry.
4. Economics

The fundamentals of supply and demand, market dynamics, economic analysis, and policy formulation are covered in depth in economics courses. Students learn to interpret economic trends, comprehend macroeconomic factors, and base decisions on economic indicators. Numerous professions, such as finance, consulting, policy-making, and market research, benefit from understanding economics.
Economics is a social science that examines how societies allocate their scarce resources to satisfy unlimited wants and needs. It is a diverse and multifaceted field with several branches and areas of specialization. Whether you are pursuing a Bachelor’s degree in Economics or taking economics courses as part of another program, here are some common economics subjects you might encounter:
1. Microeconomics: Microeconomics deals with the behavior of individual consumers, firms, and industries. Some of the topics covered in microeconomics include supply and demand, market structures (perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition), consumer theory, producer theory, and market failures.
2. Macroeconomics: Macroeconomics focuses on the overall economy and studies factors such as GDP (Gross Domestic Product), inflation, unemployment, fiscal policy, monetary policy, economic growth, and international trade.
3. Economic Theory: Economic theory provides the foundation for understanding economic concepts, principles, and models. It covers topics like utility theory, production theory, cost theory, and general equilibrium.
4. Econometrics: Econometrics involves the application of statistical methods to analyze economic data and test economic theories. It helps economists make predictions and test hypotheses using real-world data.
5. International Economics: International economics examines the economic interactions between different countries and covers topics like international trade, tariffs, exchange rates, balance of payments, and globalization.
6. Development Economics: Development economics focuses on the economic conditions and challenges faced by developing countries. It covers issues related to poverty, income distribution, economic development strategies, and foreign aid.
7. Labor Economics: Labor economics studies the behavior of labor markets, wage determination, unemployment, human capital, and labor market policies.
8. Public Economics: Public economics deals with the role of government in the economy. It includes topics such as taxation, public expenditure, public goods, and welfare economics.
9. Environmental Economics: Environmental economics analyzes the economic impact of environmental policies and studies how economic activities affect the environment.
10. Monetary Economics: Monetary economics examines the role of money, central banking, monetary policy, and its effects on the economy.
11. Behavioral Economics: Behavioral economics combines insights from psychology and economics to understand how individuals make economic decisions and how biases and cognitive limitations influence their choices.
12. Game Theory: Game theory studies strategic decision-making in situations involving multiple actors, such as firms or countries, and explores how individuals’ choices influence each other.
These are just some of the many subjects you might encounter while studying economics. The actual curriculum may vary depending on the level of study (undergraduate or graduate) and the specific focus of the economics program you are enrolled in.
5. Entrepreneurship

Entrepreneurship courses promote creativity, taking calculated risks, and starting a business. Students pick up skills for locating business opportunities, creating business plans, obtaining funding, and overcoming obstacles associated with starting and expanding a business. This course gives students the knowledge and attitude necessary to succeed as entrepreneurs or intrapreneurs within established businesses.
Entrepreneurship is the process of starting, organizing, and managing a new business venture with the aim of creating value and achieving financial success. Whether you are pursuing a degree specifically in Entrepreneurship or taking entrepreneurship courses as part of a business program, the curriculum is designed to equip students with the skills and knowledge necessary to become successful entrepreneurs.
Here are some common entrepreneurship subjects you might encounter:
1. Introduction to Entrepreneurship: An overview of the concepts, principles, and theories of entrepreneurship, including the role of entrepreneurs in the economy and society.
2. Business Planning: Developing a comprehensive business plan that outlines the business idea, target market, marketing strategy, financial projections, and operational plan.
3. New Venture Creation: Learning the process of identifying and evaluating business opportunities and turning them into viable new ventures.
4. Innovation and Creativity: Understanding the importance of innovation and creativity in entrepreneurship and exploring methods to foster innovation within a business context.
5. Entrepreneurial Finance: Learning about various sources of funding for startups and understanding financial management and budgeting for a new venture.
6. Marketing for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the fundamentals of marketing and developing effective marketing strategies to promote and grow a new business.
7. Entrepreneurial Leadership: Exploring the characteristics and behaviors of successful entrepreneurs and developing leadership skills for managing a startup.
8. Market Research and Analysis: Conducting market research to understand customer needs, analyze competition, and identify market trends to make informed business decisions.
9. Sales and Business Development: Learning the art of selling products or services and developing strategies to attract customers and grow the business.
10. Legal and Regulatory Issues for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the legal aspects of starting and running a business, including business structures, contracts, intellectual property, and compliance with regulations.
11. Entrepreneurial Ethics and Social Responsibility: Exploring ethical issues faced by entrepreneurs and understanding the importance of social responsibility in business.
12. Scaling and Growth Strategies: Developing plans and strategies for scaling the business and achieving sustainable growth.
13. Entrepreneurship in a Global Context: Understanding the challenges and opportunities of conducting business internationally and navigating the global market.
14. Managing Small Business Operations: Learning how to manage day-to-day operations efficiently and effectively to ensure the success of the business.
15. Entrepreneurial Networking and Pitching: Developing networking skills and learning how to pitch business ideas to investors, partners, and stakeholders.
These subjects provide a solid foundation for aspiring entrepreneurs and cover essential aspects of starting, managing, and growing a successful business venture. The actual curriculum may vary depending on the institution and the specific focus of the entrepreneurship program. Additionally, some programs may offer elective courses that allow students to delve deeper into specific areas of entrepreneurship based on their interests and career goals.
6. Business Analytics

Business analytics has become a crucial area in the era of data-driven decision-making. People with knowledge of business analytics can support strategic planning, business process improvement, and market research across industries. In business analytics courses, people can learn to gather, analyze, and interpret data to make wise business decisions. The skills of data visualization, statistical analysis, predictive modeling, and data-driven problem-solving are developed in the students.
Business Analytics is a field that focuses on using data analysis, statistical methods, and quantitative techniques to gain insights, make informed business decisions, and solve complex business problems. Business Analytics subjects typically cover a wide range of topics related to data analysis, data management, and data-driven decision-making. The specific subjects may vary depending on the institution and the level of study (undergraduate or graduate).
Here are some common Business Analytics subjects you might encounter:
1. Data Analysis and Visualization: Learning how to collect, clean, and analyze data using various statistical and visualization tools, such as Excel, R, Python, Tableau, or Power BI.
2. Statistics for Business Analytics: Understanding the foundational principles of statistics and how to apply statistical methods to analyze and interpret data.
3. Data Mining and Machine Learning: Exploring algorithms and techniques to discover patterns and trends in data and make predictions using machine learning models.
4. Database Management: Learning about database concepts, SQL queries, and data management best practices to handle and manipulate large datasets.
5. Predictive Analytics: Understanding how to use historical data to make predictions about future events and outcomes.
6. Descriptive Analytics: Learning how to summarize and describe data to gain insights into business performance and trends.
7. Business Intelligence: Understanding how to use data to support decision-making and improve business operations.
8. Data Warehousing: Learning about data warehousing concepts and practices to store and manage large volumes of data.
9. Optimization Models: Using mathematical modeling and optimization techniques to solve business problems and improve processes.
10. Text Analytics: Exploring methods to analyze and extract insights from unstructured text data, such as customer reviews or social media content.
11. Data Ethics and Privacy: Understanding the ethical considerations and legal implications of handling and using data in business analytics.
12. Data Governance and Quality: Learning how to ensure data integrity, quality, and security in the analytics process.
13. Business Analytics for Marketing: Applying analytics to understand customer behavior, segment markets, and optimize marketing campaigns.
14. Business Analytics for Operations: Using analytics to improve supply chain management, inventory control, and production processes.
15. Business Analytics for Finance: Analyzing financial data to make investment decisions, manage risk, and optimize financial performance.
16. Business Analytics for Strategy: Using data to support strategic decision-making and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
17. Time Series Analysis: Understanding methods for analyzing data that is collected over time, such as sales trends or stock prices.
18. Big Data Analytics: Exploring tools and techniques for analyzing large and complex datasets, often involving distributed computing and cloud technologies.
19. Web Analytics: Analyzing website data to understand user behavior, optimize web performance, and enhance online marketing efforts.
20. Data Visualization and Storytelling: Learning how to present data effectively through visualizations and communicate analytical findings to non-technical stakeholders.
Business Analytics programs often provide hands-on experience with real-world datasets and may include projects or case studies to apply the learned concepts in practical business scenarios. Additionally, some programs may offer elective courses that allow students to specialize in specific areas of business analytics based on their interests and career goals.
7. Marketing

Understanding consumer behavior, market research, brand management, and strategic marketing planning is possible thanks to marketing courses. Students learn how to define target markets, create marketing campaigns, and use a variety of channels for efficient promotion. People with marketing knowledge can work in sales, brand management, advertising, digital marketing, market research, and other related fields, influencing customer perceptions and fostering business expansion.
Marketing is a crucial aspect of business that involves understanding customer needs, creating products or services that satisfy those needs, and effectively promoting and selling them to the target audience. Marketing subjects cover a wide range of topics, from market research and consumer behavior to advertising and digital marketing. The specific subjects offered may vary depending on the institution and the level of study (undergraduate or graduate).
Here are some common marketing subjects you might encounter:
1. Principles of Marketing: An introductory course that covers the fundamental concepts and principles of marketing.
2. Consumer Behavior: Understanding the factors that influence consumer decision-making and buying behavior.
3. Market Research: Learning how to gather and analyze data to understand market trends, customer preferences, and competitors.
4. Marketing Management: Exploring marketing strategies and tactics to effectively manage the marketing function within an organization.
5. Product Management: Understanding the process of developing and managing products throughout their lifecycle.
6. Brand Management: Learning how to build, maintain, and protect a strong brand identity.
7. Advertising and Promotion: Studying various advertising techniques and promotional strategies to reach the target audience.
8. Digital Marketing: Exploring online marketing channels, including social media, SEO, content marketing, and email marketing.
9. Marketing Analytics: Using data analysis and metrics to measure marketing performance and make data-driven decisions.
10. Pricing Strategies: Understanding how to set prices for products or services to achieve marketing objectives.
11. Retail Marketing: Exploring marketing strategies specific to the retail industry and understanding consumer behavior in retail settings.
12. International Marketing: Understanding the challenges and opportunities of marketing products and services in global markets.
13. Sales Management: Learning about sales strategies, sales force management, and customer relationship management.
14. Marketing Communications: Studying integrated marketing communication methods to deliver consistent brand messages.
15. Services Marketing: Understanding the unique marketing challenges and strategies for service-based businesses.
16. Social Media Marketing: Exploring how to leverage social media platforms for marketing and customer engagement.
17. E-commerce Marketing: Understanding marketing strategies for online businesses and e-commerce platforms.
18. Public Relations: Learning how to manage and maintain a positive public image for an organization.
19. Marketing Strategy: Developing and implementing marketing plans and strategies to achieve business objectives.
20. Relationship Marketing: Understanding the importance of building long-term relationships with customers to enhance loyalty and retention.
Marketing programs often involve practical projects, case studies, and real-world simulations to provide students with hands-on experience and prepare them for marketing roles in various industries. Additionally, some programs may offer elective courses that allow students to focus on specific areas of marketing, such as digital marketing, brand management, or marketing analytics, based on their interests and career goals.
8. Business Communication

Students must enroll in business communication courses to improve their capacity to communicate proficiently with internal and external audiences, whether spoken or written. Students learn how to effectively communicate in various business contexts, including creating messages that persuade and deliver presentations. Building relationships, negotiating, and effectively expressing ideas and information depends on one’s ability in business communication.
Business Communication is a critical skill for professionals in any industry. It involves effectively conveying information, ideas, and messages within a business context to achieve specific goals. Business Communication subjects focus on various aspects of written, verbal, and nonverbal communication in professional settings. The specific subjects offered may vary depending on the institution and the level of study (undergraduate or graduate). Here are some common Business Communication subjects you might encounter:
1. Business Writing: Learning how to write clear, concise, and professional business documents, such as emails, memos, reports, and proposals.
2. Professional Speaking: Developing public speaking and presentation skills for effective communication in front of an audience.
3. Interpersonal Communication: Understanding the principles of effective communication in one-on-one or small group settings.
4. Business Negotiation: Learning how to communicate and negotiate effectively to reach mutually beneficial agreements.
5. Cross-Cultural Communication: Understanding the challenges and strategies for effective communication in a diverse and multicultural business environment.
6. Business Etiquette: Learning the norms and practices of professional behavior in business settings.
7. Persuasive Communication: Understanding the art of influencing and persuading others through communication.
8. Crisis Communication: Studying how to manage and communicate effectively during times of crisis or emergency.
9. Digital Communication: Exploring effective communication methods in the digital age, including email etiquette and online collaboration.
10. Business Communication Strategy: Developing communication plans and strategies to achieve business objectives.
11. Visual Communication: Understanding how to use visual aids and graphics to enhance communication effectiveness.
12. Team Communication: Learning how to communicate effectively within a team or project group.
13. Leadership Communication: Understanding how effective leaders communicate and inspire others.
14. Business Presentations: Practicing and refining presentation skills for delivering impactful business presentations.
15. Business Communication Ethics: Exploring ethical issues related to business communication, such as honesty, transparency, and confidentiality.
16. Conflict Resolution: Learning how to manage and resolve conflicts through effective communication.
17. Business Storytelling: Understanding the power of storytelling in business communication to engage and connect with audiences.
18. Nonverbal Communication: Studying the role of body language, facial expressions, and gestures in communication.
19. Social Media Communication: Understanding how businesses use social media for communication and branding.
20. Business Communication and Technology: Exploring communication tools and technologies used in modern business environments.
Business Communication programs often include practical exercises, role-playing, and real-world simulations to provide students with hands-on experience. Additionally, some programs may offer elective courses that allow students to focus on specific areas of business communication, such as public relations, corporate communication, or digital communication, based on their interests and career goals.
9. International Business

The difficulties of conducting business on a global scale are examined in international business courses. Students gain knowledge of international markets, trade, cultural issues, and the economic and legal ramifications of doing business internationally.
By learning how to negotiate cross-cultural communication, global supply chains, and market entry strategies, people who complete this course will be well-prepared for careers in multinational corporations, international trade organizations, and global corporations.
International Business is a field of study that focuses on the various aspects of conducting business across national borders. It involves understanding the complexities and challenges of operating in a global marketplace, where companies interact with different cultures, legal systems, political environments, and economic conditions. The subject covers a wide range of topics and disciplines that are essential for success in the international business arena.
Here are some key subjects typically covered in an International Business curriculum:
1. International Trade: This subject explores the theory, practices, and policies related to the exchange of goods and services between countries. It includes concepts like tariffs, trade agreements, trade barriers, and the impact of globalization on trade patterns.
2. International Marketing: This subject focuses on marketing strategies and tactics tailored to different cultures and markets. Students learn how to adapt products, pricing, promotion, and distribution strategies to meet the needs and preferences of consumers in diverse countries.
3. Global Finance: This subject delves into financial management in the context of international business. It covers topics like foreign exchange, international investment, managing currency risks, and understanding the complexities of global financial markets.
4. International Business Law: Students learn about the legal frameworks that govern international business transactions. This subject covers international contracts, intellectual property rights, trade regulations, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
5. Cross-Cultural Management: This subject deals with managing a diverse workforce and business relationships across different cultures. It covers aspects like communication, negotiation, leadership, and teamwork in an international setting.
6. Global Supply Chain Management: This subject focuses on the coordination and optimization of global supply chains, considering factors like transportation, logistics, sourcing, and inventory management.
7. International Economics: This subject explores the economic theories and policies that impact international trade and investment. Topics may include balance of payments, exchange rates, economic development, and global economic institutions.
8. International Business Strategy: This subject deals with formulating and implementing strategies for companies operating in the international market. It covers aspects like market entry modes, expansion strategies, and assessing the competitive landscape.
9. Emerging Markets: This subject examines the opportunities and challenges associated with doing business in emerging economies. It explores the unique aspects of these markets, including rapid growth, regulatory environments, and cultural factors.
10. Corporate Social Responsibility and Ethics in International Business: This subject addresses the ethical and social responsibilities of businesses operating globally. Students learn about sustainable business practices and managing social and environmental impacts.
These are just some of the key subjects you might encounter in an International Business program. The field is continuously evolving, and as globalization progresses, new challenges and opportunities will continue to shape the curriculum and research in this area.
10. Accounting

Accounting courses provide a foundation in financial reporting, managerial accounting, auditing, and taxation. Accounting knowledge paves the way for careers as accountants, financial analysts, auditors, or even Certified Public Accountants (CPAs), which provide insightful financial analysis and guarantee legal compliance. The interpretation of financial statements, the analysis of financial data, and ensuring standards compliance are all skills that students acquire.
Accounting is a crucial field that involves the measurement, processing, and communication of financial information about businesses and organizations. It helps stakeholders, such as management, investors, creditors, and government agencies, make informed decisions. Accounting programs typically cover a variety of subjects that provide a comprehensive understanding of financial reporting, analysis, and management.
Here are some common accounting subjects:
1. Financial Accounting: This subject focuses on the principles and procedures for preparing and presenting financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. It covers topics like revenue recognition, inventory valuation, depreciation, and accounting for various business transactions.
2. Managerial Accounting: Managerial accounting emphasizes the use of accounting information to support internal decision-making within organizations. It includes cost analysis, budgeting, performance evaluation, and relevant data for managerial planning and control.
3. Auditing: Auditing involves the examination and verification of financial records to ensure they are accurate and comply with accounting standards. Students learn auditing techniques, professional ethics, and how to express audit opinions.
4. Taxation: This subject focuses on the principles and practices of tax law and its application to individuals and businesses. Students learn about income tax, corporate tax, tax planning, and tax compliance.
5. Financial Statement Analysis: This subject teaches students how to interpret financial statements to assess a company’s financial performance, liquidity, solvency, and profitability. Ratio analysis and other financial tools are used to evaluate the financial health of an organization.
6. Cost Accounting: Cost accounting deals with the measurement, analysis, and allocation of costs to products, services, or projects. It provides valuable information for management in making decisions related to pricing, production, and resource allocation.
7. Accounting Information Systems: This subject covers the design, implementation, and use of accounting information systems to collect, process, and report financial data. It explores the role of technology in modern accounting practices.
8. Financial Management: While closely related to accounting, financial management goes beyond accounting and focuses on making financial decisions to maximize shareholder value. It includes topics like capital budgeting, capital structure, and working capital management.
9. International Accounting: International accounting examines accounting practices and standards in a global context, considering differences in reporting and compliance requirements across countries.
10. Forensic Accounting: This subject combines accounting, auditing, and investigative skills to detect and prevent financial fraud, misconduct, and irregularities.
11. Government and Nonprofit Accounting: This subject covers accounting principles specific to governmental and nonprofit entities, including fund accounting and financial reporting for public sector organizations.
These are some of the core subjects commonly found in accounting programs. Depending on the level of the course (undergraduate or graduate) and the specific focus of the program, additional advanced topics may be included, such as advanced financial reporting, mergers and acquisitions, sustainability accounting, and corporate governance.
11. Supply Chain Management
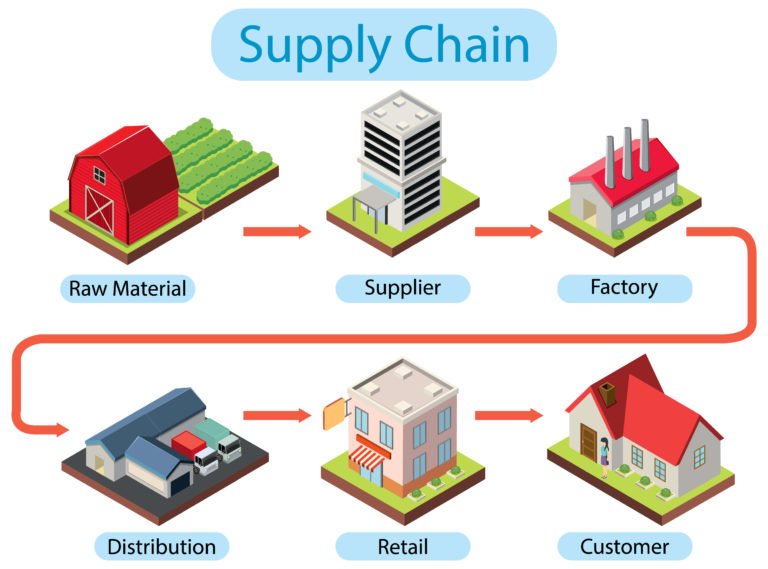
Supply Chain Management (SCM) courses concentrate on the efficient flow of goods, services, and information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. Students learn about inventory management, supply chain optimization, logistics, and purchasing. People who are knowledgeable about SCM help organizations and supply chain networks streamline operations, cut costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the management and coordination of the flow of goods, services, information, and finances across the entire supply chain, from raw material suppliers to end customers. SCM plays a critical role in ensuring the efficiency, effectiveness, and competitiveness of businesses. The subjects covered in SCM programs vary depending on the level of study and the specific focus of the curriculum.
Here are some common supply chain management subjects:
1. Introduction to Supply Chain Management: This subject provides an overview of supply chain management, its importance, and its role in the business environment. It covers the key components and functions of supply chains.
2. Operations Management: Operations management is an essential aspect of supply chain management. This subject focuses on managing production processes, inventory, quality control, and capacity planning.
3. Logistics Management: Logistics involves the planning, implementation, and control of the efficient movement and storage of goods, services, and information from point of origin to the point of consumption. Students learn about transportation, warehousing, order fulfillment, and distribution strategies.
4. Inventory Management: Inventory management focuses on maintaining optimal levels of inventory to meet customer demand while minimizing holding costs. Students learn about inventory control models, reorder points, safety stock, and just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems.
5. Procurement and Supplier Management: This subject covers the processes involved in sourcing and procuring raw materials, goods, and services from suppliers. It includes supplier selection, negotiation, contract management, and supplier relationship management.
6. Demand Forecasting and Planning: Demand forecasting is essential for supply chain management to align production and inventory levels with customer demand. This subject covers various forecasting methods and their application in planning processes.
7. Supply Chain Analytics: Supply chain analytics involves using data and quantitative methods to analyze and optimize supply chain operations. Students learn about data-driven decision-making, performance metrics, and using software tools for analysis.
8. Supply Chain Sustainability: This subject addresses the social, environmental, and ethical dimensions of supply chain management. Students learn about sustainable practices, green supply chain initiatives, and corporate social responsibility.
9. Supply Chain Risk Management: Supply chains are vulnerable to various risks, including disruptions, natural disasters, and geopolitical uncertainties. This subject covers strategies for identifying, assessing, and mitigating supply chain risks.
10. Global Supply Chain Management: This subject focuses on the unique challenges and opportunities associated with managing supply chains in a global context. It covers international trade, cultural considerations, and global logistics.
11. Supply Chain Strategy: Supply chain strategy involves aligning supply chain decisions with overall business strategy. Students learn how to design and implement effective supply chain strategies that support organizational goals.
12. Supply Chain Collaboration and Coordination: This subject explores the importance of collaboration among supply chain partners and the use of technology to facilitate coordination and information sharing.
These subjects provide a comprehensive understanding of supply chain management and equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in the dynamic and complex field of supply chain management.
12. Human Resource Management

Human resource management (HRM) courses focus primarily on managing an organization’s most valuable asset—its people. Employee development, compensation and benefits administration, and employment law are covered in class. HR specialists are essential for attracting and keeping top talent, creating a positive workplace culture, and increasing employee motivation and productivity.
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a critical function within organizations that focuses on managing and developing human resources to achieve business goals and enhance employee performance and well-being. HRM programs typically cover a wide range of subjects to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of managing human capital effectively.
Here are some common Human Resource Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Human Resource Management: This subject provides an overview of the HRM function, its role in organizations, and the various HR processes and practices.
2. Human Resource Planning and Staffing: HR planning involves forecasting workforce needs, conducting job analyses, and developing recruitment and selection strategies to attract and hire the right talent.
3. Employee Training and Development: This subject focuses on designing and implementing training programs to enhance employee skills and knowledge, as well as fostering continuous learning and development.
4. Performance Management: Performance management involves setting performance expectations, conducting performance appraisals, providing feedback, and developing performance improvement plans.
5. Compensation and Benefits: Students learn about designing competitive compensation packages, including salary structures, incentives, and employee benefits to attract and retain talent.
6. Employee Relations and Labor Law: This subject covers managing employee relations, handling grievances, understanding labor laws, and ensuring compliance with employment regulations.
7. Talent Management and Succession Planning: Talent management involves identifying and nurturing high-potential employees and developing plans for succession and leadership development.
8. Diversity and Inclusion in the Workplace: This subject addresses creating an inclusive and diverse work environment, understanding diversity challenges, and promoting equal opportunities for all employees.
9. Employee Engagement and Motivation: Students learn about strategies to boost employee engagement, increase motivation, and foster a positive work culture.
10. HR Metrics and Analytics: HR metrics and analytics involve using data to measure HR effectiveness and make data-driven decisions in areas such as recruitment, retention, and employee performance.
11. Organizational Development: This subject focuses on managing change within organizations, understanding organizational behavior, and implementing strategies for organizational improvement.
12. HR Information Systems (HRIS): HRIS subjects cover the use of technology for managing HR processes, including HR databases, payroll systems, and employee self-service portals.
13. Workplace Health and Safety: This subject addresses occupational health and safety regulations, workplace wellness programs, and ensuring a safe and healthy work environment.
14. Employment Law and Regulations: Students learn about various employment laws and regulations, including labor laws, anti-discrimination laws, and employee rights.
15. International HRM: International HRM covers HR challenges and strategies in a global context, including managing a diverse and culturally different workforce.
These subjects equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to handle the complexities and challenges of managing human resources effectively and contribute to the success of organizations as HR professionals.
13. Project Management
Individuals who take project management courses gain the ability to efficiently plan, carry out, and keep track of projects from start to finish. Students gain knowledge of project management techniques, risk analysis, budgeting, and teamwork. People with project management skills can manage teams, guarantee projects are successful, and accomplish organizational goals while staying within a specific time, scope, and budget constraints.
Project Management is the discipline of planning, organizing, and managing resources to successfully complete specific projects within defined constraints, such as scope, time, budget, and quality. Project management subjects typically cover a wide range of topics to provide students with the skills and knowledge necessary to effectively lead and execute projects. Here are some common Project Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Project Management: This subject provides an overview of project management principles, methodologies, and best practices. It introduces students to the project management lifecycle and key project management processes.
2. Project Scope Management: Scope management involves defining the project’s objectives, deliverables, and boundaries. Students learn how to create a project scope statement and manage scope changes throughout the project.
3. Project Time Management: This subject covers the techniques for scheduling project activities, creating project timelines, and managing project schedules to ensure timely project completion.
4. Project Cost Management: Cost management involves estimating, budgeting, and controlling project costs. Students learn how to develop project budgets and monitor expenses during project execution.
5. Project Quality Management: Quality management focuses on ensuring that the project’s deliverables meet the required standards and meet stakeholder expectations. Students learn about quality planning, assurance, and control.
6. Project Risk Management: This subject addresses identifying, analyzing, and mitigating project risks. Students learn how to develop risk management plans and respond to potential risks that may impact the project.
7. Project Communication Management: Effective communication is crucial for project success. This subject covers communication planning, stakeholder engagement, and managing project communication channels.
8. Project Human Resource Management: Human resource management in projects involves acquiring, developing, and managing the project team. Students learn about team building, motivation, and conflict resolution.
9. Project Procurement Management: Procurement management deals with the acquisition of goods and services from external vendors. Students learn about procurement planning, vendor selection, and contract management.
10. Project Integration Management: Integration management focuses on coordinating all project management processes and ensuring that project activities align with the project’s objectives.
11. Agile Project Management: This subject introduces Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, and their application in managing projects with changing requirements and iterative development.
12. Project Leadership and Ethics: Project leadership covers leadership styles, ethical considerations, and the role of project managers in motivating and inspiring project teams.
13. Project Stakeholder Management: Stakeholder management involves identifying and engaging project stakeholders, addressing their needs, and managing their influence on the project.
14. Project Management Tools and Software: Students learn how to use project management software and tools for scheduling, budgeting, collaboration, and reporting.
15. Project Closure and Lessons Learned: This subject covers the processes for closing a project, conducting project reviews, and documenting lessons learned for future projects.
These subjects provide a comprehensive understanding of project management principles and practices, preparing students to excel as project managers in various industries and organizational settings.
14. Strategic Management

Long-term organizational strategies are the main topic of study in strategic management courses. Students learn to evaluate internal and external environments, assess competition, and develop sustainable business growth strategies. Strategic management expertise helps people become adept at coordinating business objectives with market opportunities and guiding organizations toward success.
Strategic Management is the process of formulating and implementing strategies to achieve an organization’s long-term goals and objectives. It involves analyzing the internal and external environment, setting strategic direction, making decisions, and allocating resources to gain a sustainable competitive advantage. Strategic Management subjects cover various aspects of strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation.
Here are some common Strategic Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Strategic Management: This subject provides an overview of the strategic management process, its importance, and its role in organizational success.
2. Strategic Analysis: Strategic analysis involves assessing the organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as the opportunities and threats in the external environment. Students learn various tools and techniques to conduct a thorough analysis.
3. Business and Corporate Strategy: This subject covers the different levels of strategy, including business-level strategy (how to compete in specific markets) and corporate-level strategy (decisions about the company’s overall scope and portfolio of businesses).
4. Strategic Planning: Strategic planning involves formulating specific action plans to achieve the organization’s strategic objectives. Students learn about goal-setting, action plans, and resource allocation.
5. Strategic Implementation and Execution: This subject focuses on the process of translating strategic plans into action. Students learn about aligning organizational structures, systems, and processes with the chosen strategies.
6. Strategic Leadership: Strategic leadership involves guiding and influencing the organization to effectively execute the strategic vision. This subject covers leadership styles, change management, and decision-making in a strategic context.
7. Strategic Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Students learn how to foster innovation and entrepreneurial initiatives to create new opportunities and competitive advantages for the organization.
8. Strategic Marketing: Strategic marketing involves developing marketing strategies that align with the overall strategic objectives of the organization. It covers market analysis, segmentation, positioning, and marketing planning.
9. Strategic Human Resource Management: This subject addresses aligning HR practices with strategic goals, including talent acquisition, development, performance management, and workforce planning.
10. Strategic Financial Management: Strategic financial management involves aligning financial decisions with the organization’s strategic goals. Students learn about financial planning, capital budgeting, and financial risk management.
11. Strategic Change Management: This subject covers managing organizational change resulting from strategic initiatives, including overcoming resistance and ensuring successful implementation.
12. Strategic Alliances and Partnerships: Students learn about forming strategic alliances and partnerships to leverage external resources, capabilities, and markets.
13. Corporate Governance and Ethics: This subject addresses ethical considerations in strategic decision-making and the role of corporate governance in ensuring responsible management practices.
14. Strategic Performance Measurement and Control: This subject covers measuring and evaluating the success of strategic initiatives using performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs).
15. International and Global Strategy: Students learn about formulating strategies to expand into international markets and manage global operations effectively.
These subjects equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to be effective strategic leaders, helping organizations gain a competitive edge and thrive in a dynamic and competitive business environment.
15. Operations Management

The effective planning, coordinating, and control of organizational processes are covered in depth in operations management courses. Students study production methods, supply chain planning, quality control, and process enhancement. The productivity, cost, and operational efficiency of individuals with operations management skills can be improved across industries.
Operations Management is a field that focuses on the design, planning, and control of the processes that transform inputs (such as materials, labor, and technology) into goods and services. It plays a crucial role in managing the production and delivery of products and services efficiently and effectively. Operations Management subjects cover various aspects of managing operations in organizations.
Here are some common Operations Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Operations Management: This subject provides an overview of operations management principles, concepts, and its role in organizations.
2. Operations Strategy: Operations strategy involves aligning operational decisions with the overall business strategy. Students learn about designing and implementing effective operations strategies to achieve competitive advantage.
3. Process Design and Analysis: This subject covers the design, analysis, and improvement of business processes to enhance efficiency and productivity.
4. Capacity Planning: Capacity planning involves determining the optimal production capacity to meet current and future demand requirements.
5. Quality Management: Quality management focuses on ensuring that products and services meet customer expectations. Students learn about quality control, total quality management (TQM), and continuous improvement methodologies.
6. Supply Chain Management: Supply chain management addresses the coordination and optimization of the flow of goods, services, and information from suppliers to end customers.
7. Inventory Management: This subject covers managing inventory levels to balance production and demand, minimize costs, and ensure smooth operations.
8. Lean Manufacturing: Lean principles aim to eliminate waste and improve efficiency in manufacturing processes. Students learn about lean tools and techniques such as 5S, Kaizen, and value stream mapping.
9. Project Management: Operations managers may need to handle projects related to process improvement or product development. Project management subjects cover the principles and techniques of successful project execution.
10. Production Planning and Control: Production planning involves scheduling and coordinating production activities to meet customer demand and optimize resource utilization.
11. Service Operations Management: This subject focuses on managing the unique challenges of service-oriented operations, such as capacity planning, service quality, and service delivery.
12. Maintenance Management: Maintenance management involves planning and executing maintenance activities to ensure the reliability and longevity of equipment and assets.
13. Operations Research: Operations research subjects use mathematical and analytical methods to optimize operational processes, resource allocation, and decision-making.
14. Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a methodology used to improve process quality by reducing defects and variations. Students learn about Six Sigma tools and methodologies.
15. Sustainability and Green Operations: This subject addresses integrating sustainable practices into operations to reduce environmental impact and enhance social responsibility.
These subjects equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively manage operations in various industries and organizations, contributing to increased efficiency, quality, and competitiveness.
16. Information Systems Management

Information systems management courses emphasize the fusion of technological and organizational processes. Enterprise systems, cybersecurity, and digital transformation are taught to students. One can ensure efficient information flow and data security by bridging the gap between business needs and technological solutions with knowledge of information systems management.
Information Systems Management is a field that focuses on the planning, implementation, and utilization of information technology to support and enhance organizational processes and decision-making. It involves managing various aspects of information systems, including hardware, software, databases, networks, and cybersecurity. Information Systems Management subjects cover a wide range of topics to provide students with the skills and knowledge needed to effectively manage IT resources within organizations.
Here are some common Information Systems Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Information Systems Management: This subject provides an overview of information systems, their role in organizations, and the key concepts and frameworks in IS management.
2. Information Technology Strategy and Planning: IT strategy involves aligning IT initiatives with the overall business strategy. Students learn about IT planning, governance, and the strategic role of IT in organizations.
3. Database Management: This subject covers the design, implementation, and administration of databases to store and manage organizational data effectively.
4. Business Intelligence and Analytics: Students learn about using data analysis and business intelligence tools to extract valuable insights from data and support decision-making.
5. IT Project Management: IT project management focuses on planning, executing, and controlling IT projects to deliver solutions on time and within budget.
6. IT Service Management: IT service management addresses the processes and practices for delivering and managing IT services to meet the needs of the organization and its users.
7. Cybersecurity and Information Assurance: This subject covers the protection of information and IT systems from cyber threats, data breaches, and other security risks.
8. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: Students learn about the implementation and management of ERP systems to integrate various business processes and functions.
9. IT Infrastructure Management: IT infrastructure management involves the planning, deployment, and maintenance of hardware, software, networks, and cloud computing resources.
10. E-Commerce and Digital Business: This subject explores the management of electronic commerce platforms and the use of digital technologies to conduct business online.
11. IT Governance and Risk Management: IT governance subjects cover the framework for making IT-related decisions and managing IT-related risks.
12. Mobile and Cloud Computing: Students learn about the use of mobile devices and cloud-based technologies to support business processes and enhance flexibility.
13. Emerging Technologies: This subject addresses the latest trends and developments in information technology, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
14. IT Ethics and Legal Issues: This subject covers ethical considerations and legal aspects related to the use of IT systems and data.
15. Information Systems Audit and Compliance: Students learn about auditing information systems and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
These subjects prepare students to manage and leverage information technology to support business objectives, improve processes, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving digital environment.
17. Digital Marketing
Courses on digital marketing examine the methods and approaches used to advertise goods and services online. Students study digital advertising, content marketing, search engine optimization, and social media marketing. Expertise in digital marketing is highly sought after by companies looking to establish their online presence and effectively reach target audiences due to the rapid growth of online platforms.
18. Sales Management

The main topics covered in sales management courses are the fundamentals of successful sales strategies, client relationship management, and sales team leadership. Prospecting, negotiation, sales analytics, and managing sales processes are among the topics students cover. People skilled in sales management can increase revenue, manage customer relations, and motivate sales teams to hit goals.
Sales Management is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling sales activities to achieve the organization’s sales targets and objectives. It involves managing the sales team, setting sales strategies, and monitoring sales performance. Sales Management subjects cover various aspects of managing the sales function effectively. Here are some common Sales Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Sales Management: This subject provides an overview of sales management principles, the role of sales managers, and the importance of the sales function in achieving organizational goals.
2. Sales Strategy and Planning: Sales strategy involves formulating plans to achieve sales targets and objectives. Students learn about market analysis, customer segmentation, and sales forecasting.
3. Sales Team Management: This subject covers recruiting, training, and motivating the sales team to enhance performance and achieve sales targets.
4. Sales Techniques and Selling Skills: Students learn various selling techniques, negotiation skills, and relationship-building strategies to close deals successfully.
5. Sales Performance Metrics and KPIs: This subject addresses measuring and evaluating sales performance using key performance indicators (KPIs) and sales metrics.
6. Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRM subjects cover the use of CRM tools and systems to manage customer information, track leads, and enhance customer interactions.
7. Sales Territory Management: Sales territory management involves dividing markets into manageable areas and assigning sales representatives to specific territories.
8. Sales Forecasting and Demand Planning: Students learn about techniques for predicting future sales demand and aligning production and inventory levels accordingly.
9. Sales Promotion and Incentive Programs: This subject covers designing and implementing sales promotion strategies and incentive programs to motivate the sales team and boost sales.
10. Key Account Management: Key account management focuses on managing relationships with high-value customers to maximize sales and build long-term partnerships.
11. Sales Communication and Presentation Skills: Students learn effective communication and presentation techniques to articulate value propositions and persuade customers.
12. Sales Channel Management: This subject addresses managing different sales channels, such as direct sales, online sales, and channel partner management.
13. Sales Ethics and Professionalism: Sales ethics subjects cover ethical considerations in sales practices and maintaining professionalism in customer interactions.
14. Sales Forecasting and Budgeting: Students learn about budgeting sales expenses and developing sales forecasts to support financial planning.
15. Sales Force Automation and Technology: This subject covers the use of technology and sales automation tools to streamline sales processes and improve productivity.
These subjects provide students with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively manage sales teams, develop sales strategies, and drive revenue growth for organizations. Sales management professionals play a crucial role in achieving sales targets and building strong customer relationships.
19. Risk Management

Business operations risks are identified, evaluated, and mitigated in depth in risk management courses. Students gain knowledge of regulatory compliance, risk analysis, and risk mitigation techniques. People with knowledge of risk management assist organizations in identifying potential threats, creating backup plans, and mitigating financial and operational risks.
Risk Management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that may impact an organization’s objectives and operations. It involves analyzing risks, implementing strategies to manage or reduce them, and monitoring their effectiveness. Risk Management subjects cover various aspects of identifying, analyzing, and responding to risks in different contexts. Here are some common Risk Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Risk Management: This subject provides an overview of risk management principles, concepts, and frameworks.
2. Risk Identification: Students learn how to identify and categorize risks that could affect the organization’s projects, operations, or strategic initiatives.
3. Risk Assessment and Analysis: This subject covers techniques for assessing the probability and impact of identified risks to prioritize and quantify their potential effects.
4. Risk Response Planning: Students learn how to develop risk response plans to address identified risks effectively.
5. Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): ERM subjects focus on the integrated approach to managing risks across the entire organization, considering both strategic and operational risks.
6. Financial Risk Management: This subject addresses managing financial risks, including market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk.
7. Project Risk Management: Project risk management involves identifying and managing risks specific to projects, such as schedule delays, cost overruns, and scope changes.
8. Operational Risk Management: Students learn how to identify and mitigate risks associated with day-to-day operations and processes within the organization.
9. Cybersecurity Risk Management: This subject covers managing risks related to information security and protecting the organization against cyber threats.
10. Supply Chain Risk Management: Students learn about identifying and managing risks within the supply chain, such as disruptions in the supply chain, vendor risks, and demand volatility.
11. Business Continuity Planning: Business continuity planning subjects address preparing for and responding to potential disruptions to ensure the organization can continue operations during emergencies.
12. Crisis Management: This subject covers developing plans and strategies to manage and mitigate the impact of crises on the organization.
13. Legal and Regulatory Risk Management: Students learn about identifying and complying with legal and regulatory requirements to mitigate legal and compliance risks.
14. Reputational Risk Management: Reputational risk subjects address protecting and enhancing the organization’s reputation in the face of potential negative events.
15. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Risk Management: This subject covers managing risks related to environmental, social, and governance factors that can impact the organization’s long-term sustainability and reputation.
These subjects equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively identify, assess, and manage risks in various organizational contexts, helping organizations to make informed decisions and improve resilience in a dynamic and uncertain environment.
20. Business Law

Business law classes teach students the laws and rules of business operations. Contracts, intellectual property, employment law, and ethics are all taught to students. Individuals who are knowledgeable about business law are better equipped to make wise business decisions, ensure legal compliance, and defend the interests of organizations.
Business Law, also known as Commercial Law or Business Legal Studies, encompasses the legal principles and regulations that govern various aspects of business activities. It is crucial for business professionals to have a comprehensive understanding of business law to ensure compliance, protect rights, and make informed decisions. Business Law subjects cover a wide range of topics related to business transactions, contracts, legal structures, and regulatory compliance. Here are some common Business Law subjects:
1. Introduction to Business Law: This subject provides an overview of the legal system and its relevance to business operations.
2. Contract Law: Contract law covers the principles and elements of valid contracts, contract formation, performance, breach, and remedies for contract disputes.
3. Business Organization and Corporate Law: This subject covers different legal structures for businesses, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs).
4. Commercial Transactions: Students learn about the legal aspects of commercial transactions, including sales, leases, and negotiable instruments.
5. Intellectual Property Law: Intellectual property law addresses the protection of trademarks, copyrights, patents, and trade secrets.
6. Employment Law: This subject covers laws related to hiring, employment contracts, workplace discrimination, termination, and employee rights.
7. Labor Law: Labor law focuses on the legal relationship between employers, employees, and labor unions, including collective bargaining and labor disputes.
8. Antitrust and Competition Law: Antitrust laws address unfair business practices and prevent monopolies and anti-competitive behavior.
9. Consumer Protection Law: Students learn about laws that protect consumers from unfair business practices, false advertising, and product liability.
10. International Business Law: This subject explores the legal aspects of international business transactions, cross-border contracts, and resolving disputes in a global context.
11. Business Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility: Students learn about ethical considerations and corporate social responsibility in business practices.
12. Securities Law: Securities law covers regulations related to the issuance, sale, and trading of securities and financial instruments.
13. Environmental Law and Sustainability: This subject addresses legal regulations related to environmental protection and sustainable business practices.
14. Tax Law: Tax law covers the legal requirements and obligations related to business taxes, including income tax, sales tax, and corporate tax.
15. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Law: Students learn about legal requirements related to data protection, privacy, and cybersecurity for businesses.
These subjects provide students with a solid foundation in business law, enabling them to navigate legal issues, make sound business decisions, and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations in their professional endeavors.
21. Leadership and Management

Developing leadership abilities and efficient management techniques are the main topics covered in leadership and management courses. Organizational behavior, team dynamics, motivation, and change management are all topics that students study. Individuals can motivate teams, stimulate innovation, and promote a positive workplace culture by possessing strong leadership and management skills.
Leadership and Management are crucial aspects of any organization, as they involve guiding and directing people to achieve organizational goals effectively and efficiently. Leadership focuses on inspiring and influencing others, while management involves planning, organizing, and coordinating resources to achieve specific objectives. Leadership and Management subjects cover various skills and principles essential for successful leadership and effective management.
Here are some common Leadership and Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Leadership and Management: This subject provides an overview of leadership and management principles, their roles, and their impact on organizational success.
2. Leadership Theories and Styles: Students learn about different leadership theories and styles, including transformational, transactional, servant, and authentic leadership.
3. Organizational Behavior: Organizational behavior subjects cover the study of individual and group behavior in organizations and how leaders can influence and motivate employees.
4. Strategic Leadership: This subject focuses on aligning leadership actions with the organization’s strategic goals and vision.
5. Communication and Interpersonal Skills: Students learn effective communication techniques and interpersonal skills necessary for successful leadership and management.
6. Emotional Intelligence and Leadership: Emotional intelligence subjects cover understanding and managing emotions to improve leadership effectiveness.
7. Decision-Making and Problem-Solving: This subject addresses decision-making processes and problem-solving skills to address organizational challenges.
8. Motivation and Employee Engagement: Students learn about motivating and engaging employees to improve performance and job satisfaction.
9. Conflict Resolution and Negotiation: This subject covers resolving conflicts and negotiation skills to manage disagreements effectively.
10. Leading Change and Innovation: Students learn how to lead organizational change initiatives and foster innovation within the organization.
11. Time Management and Productivity: Time management subjects cover techniques for managing time effectively and enhancing personal productivity.
12. Performance Management: This subject addresses setting performance goals, conducting performance evaluations, and providing feedback to improve employee performance.
13. Ethics and Leadership: Students learn about ethical considerations and moral principles in leadership and decision-making.
14. Team Building and Collaboration: Team building subjects cover creating and leading high-performing teams to achieve common goals.
15. Talent Development and Succession Planning: This subject focuses on identifying and developing talent within the organization for future leadership roles.
These subjects equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge to lead and manage people, projects, and organizations effectively. Leadership and management professionals play a critical role in driving organizational success, fostering a positive work culture, and achieving strategic objectives.
22. Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior courses examine the dynamics of people’s behavior there. Students gain knowledge of organizational culture, leadership styles, motivation, and individual and group behavior. By understanding organizational behavior, individuals can better manage interpersonal relationships, form cohesive teams, and foster a positive work environment.
Organizational Behavior is a field of study that examines the behavior of individuals and groups within organizations and how it influences organizational performance and effectiveness. It involves understanding various psychological, sociological, and behavioral aspects of employees and their interactions within the workplace. Organizational Behavior subjects cover a wide range of topics to provide students with insights into human behavior in organizations. Here are some common Organizational Behavior subjects:
1. Introduction to Organizational Behavior: This subject provides an overview of organizational behavior principles, theories, and their relevance in understanding workplace dynamics.
2. Individual Behavior in Organizations: Students learn about individual factors such as personality, attitudes, motivation, perception, and learning that influence employee behavior.
3. Group Dynamics: This subject covers the behavior of individuals in groups, team development, group norms, and group decision-making processes.
4. Communication in Organizations: Students learn about effective communication patterns and strategies to improve organizational communication and information flow.
5. Leadership and Power: This subject addresses leadership styles, sources of power, and their impact on employee behavior and organizational outcomes.
6. Organizational Culture and Climate: Students learn about the influence of organizational culture and climate on employee attitudes and behavior.
7. Organizational Change and Development: This subject covers managing organizational change, resistance to change, and the role of organizational development in improving effectiveness.
8. Conflict Management and Negotiation: Students learn about strategies for managing and resolving conflicts in organizations and negotiation skills.
9. Diversity and Inclusion in the Workplace: This subject addresses the impact of diversity and inclusion on employee behavior and organizational performance.
10. Employee Engagement and Job Satisfaction: Students learn about factors that contribute to employee engagement and job satisfaction, and their effects on productivity.
11. Organizational Stress and Well-being: This subject explores the causes and consequences of workplace stress and strategies to promote employee well-being.
12. Organizational Citizenship Behavior: Students learn about voluntary behaviors that go beyond job requirements and contribute to organizational effectiveness.
13. Employee Motivation and Reward Systems: This subject covers theories of employee motivation and how reward systems influence employee behavior.
14. Organizational Ethics and Corporate Social Responsibility: Students learn about ethical considerations in organizational behavior and the role of corporate social responsibility.
15. Organizational Behavior Research and Analysis: This subject focuses on research methods used in studying organizational behavior, data analysis, and interpreting research findings.
These subjects help students understand the complexities of human behavior in organizations and provide insights into how to create a positive work environment, improve employee satisfaction, and enhance organizational performance. Organizational behavior knowledge is valuable for managers and leaders in managing teams, building effective work relationships, and promoting a productive and harmonious workplace.
23. Corporate Finance

Corporate finance courses examine how businesses make financial decisions. The concepts of capital budgeting, financial analysis, risk management, and capital structure are taught to students. People knowledgeable about corporate finance can help with strategic financial planning, investment choices, and maximizing shareholder value.
Corporate Finance is a field of study that focuses on the financial decisions and strategies made by corporations to maximize shareholder value and achieve their financial goals. It involves managing financial resources, making investment decisions, and raising capital to fund business operations and growth. Corporate Finance subjects cover various aspects of financial management within corporations. Here are some common Corporate Finance subjects:
1. Financial Management Principles: This subject provides an overview of financial management principles, concepts, and the role of finance in corporate decision-making.
2. Financial Statement Analysis: Students learn how to analyze financial statements to assess a company’s financial performance, liquidity, solvency, and profitability.
3. Capital Budgeting: Capital budgeting subjects cover techniques for evaluating and selecting investment projects that provide the best return on investment.
4. Cost of Capital and Capital Structure: This subject addresses determining the cost of capital and the optimal capital structure for a company.
5. Dividend Policy: Students learn about dividend decisions and the impact of dividend policy on shareholders and the company’s value.
6. Working Capital Management: Working capital management involves managing short-term assets and liabilities to ensure smooth business operations.
7. Long-term Financing: This subject covers various sources of long-term financing, such as equity, debt, and hybrid instruments.
8. Corporate Valuation: Students learn about different methods of valuing companies, including discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis and comparable company analysis.
9. Risk Management and Derivatives: This subject addresses managing financial risks and using derivatives to hedge against market fluctuations.
10. Mergers and Acquisitions: Students learn about the financial considerations, valuation, and financing involved in mergers and acquisitions.
11. Corporate Governance: Corporate governance subjects cover the principles and practices of corporate governance and its role in ensuring effective financial management.
12. International Finance: This subject focuses on financial management in a global context, considering foreign exchange risk and international capital markets.
13. Corporate Restructuring: Students learn about financial restructuring strategies, including divestitures, spin-offs, and debt restructuring.
14. Initial Public Offerings (IPOs): This subject covers the process of going public and raising capital through an IPO.
15. Financial Modeling and Analysis: Students learn about financial modeling techniques to support decision-making and strategic planning.
These subjects provide students with the knowledge and skills necessary to make sound financial decisions, manage corporate finances effectively, and enhance shareholder value. Corporate finance professionals play a critical role in guiding financial strategies, allocating resources, and ensuring the financial health and success of the organization.
24. Retail Management
Courses in retail management concentrate on the particular difficulties and tactics involved in running a retail operation. Students gain knowledge of retail marketing, store operations, customer service, and merchandising. Individuals with expertise in retail management are better equipped to succeed in the fast-paced retail sector and provide exceptional customer experiences.
Retail Management is a specialized field of study that focuses on the processes and strategies involved in running a retail business effectively. It covers various aspects of managing retail operations, including merchandising, customer service, inventory management, and marketing. Retail Management subjects are designed to provide students with the skills and knowledge necessary to succeed in the dynamic and competitive retail industry. Here are some common Retail Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Retail Management: This subject provides an overview of retail management principles, the role of retail in the economy, and key trends in the retail industry.
2. Retail Marketing and Consumer Behavior: Students learn about retail marketing strategies, customer segmentation, and consumer behavior to attract and retain customers.
3. Merchandising and Assortment Planning: This subject covers product assortment planning, inventory management, and visual merchandising to optimize product offerings and boost sales.
4. Store Operations Management: Students learn about managing store operations, staffing, store layout, and store performance metrics.
5. Retail Sales Management: This subject addresses sales techniques, customer engagement, and strategies for improving sales performance.
6. Retail Supply Chain Management: Retail supply chain subjects cover managing the flow of goods from suppliers to customers and optimizing supply chain efficiency.
7. Retail Pricing and Promotion: This subject covers pricing strategies, promotional campaigns, and the use of discounts and coupons to drive sales.
8. Customer Service in Retail: Students learn about providing exceptional customer service and handling customer complaints and inquiries.
9. E-commerce and Omni-channel Retailing: This subject focuses on managing online retail channels and integrating them with brick-and-mortar stores for seamless customer experiences.
10. Retail Analytics: Retail analytics subjects cover the use of data and metrics to analyze retail performance and make data-driven decisions.
11. Retail Leadership and Team Management: This subject addresses leadership skills, team building, and managing retail employees effectively.
12. Retail Brand Management: Students learn about building and maintaining a strong retail brand image to differentiate the store from competitors.
13. Retail Business Strategy: This subject focuses on developing retail business strategies that align with market opportunities and competitive advantage.
14. Store Layout and Visual Merchandising: Students learn about store layout design and visual merchandising techniques to enhance the shopping experience.
15. Retail Store Security and Loss Prevention: This subject covers security measures and loss prevention strategies to protect the store from theft and fraud.
These subjects provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the retail industry and equip them with the skills needed to manage retail operations, drive sales, and create a positive shopping experience for customers. Retail management professionals play a crucial role in meeting customer demands, optimizing profitability, and staying competitive in the retail market.
25. Hospitality and Tourism Management

Courses in hospitality and tourism management give students insights into running lodging establishments like hotels, restaurants, resorts, and travel agencies. Students gain knowledge of event planning, guest services, and tourism marketing. People skilled in hospitality and tourism management can pursue rewarding careers in the booming hospitality sector, meeting the needs of tourists and providing them with unique experiences.
Hospitality and Tourism Management is a field that focuses on managing businesses in the hospitality and tourism industry. It involves overseeing various aspects of hospitality operations, such as hotels, restaurants, resorts, travel agencies, and tourism destinations. Hospitality and Tourism Management subjects cover a wide range of topics to prepare students for leadership roles in this dynamic and customer-oriented industry.
Here are some common Hospitality and Tourism Management subjects:
1. Introduction to Hospitality and Tourism Management: This subject provides an overview of the hospitality and tourism industry, its components, and its significance in the global economy.
2. Hospitality Marketing and Sales: Students learn about marketing strategies, advertising, and sales techniques specific to the hospitality and tourism industry.
3. Hotel and Resort Management: This subject covers the management of hotels and resorts, including front office operations, housekeeping, food and beverage management, and revenue management.
4. Restaurant Management: Students learn about restaurant operations, menu planning, service standards, and customer satisfaction in restaurant settings.
5. Tourism Destination Management: This subject focuses on managing tourism destinations, including attractions, tour planning, and sustainable tourism practices.
6. Travel Agency and Tour Operations Management: Students learn about travel agency operations, tour package development, and managing travel-related services.
7. Hospitality Human Resource Management: This subject addresses recruiting, training, and managing a diverse workforce in the hospitality and tourism industry.
8. Event Management: Event management subjects cover planning and organizing events, conferences, and meetings in the hospitality sector.
9. Food and Beverage Management: Students learn about managing food and beverage operations, including inventory control, menu pricing, and quality standards.
10. Hospitality Finance and Accounting: This subject covers financial management and accounting principles specific to the hospitality and tourism industry.
11. Hospitality Technology and Information Systems: Students learn about using technology and information systems to enhance guest experiences and streamline hospitality operations.
12. Cross-Cultural Management in Hospitality: This subject addresses the cultural diversity within the hospitality industry and managing international guests.
13. Sustainable Tourism and Eco-friendly Practices: Students learn about sustainable tourism practices and the importance of responsible tourism management.
14. Customer Service and Guest Relations: This subject focuses on providing excellent customer service and handling guest inquiries and complaints.
15. Hospitality Law and Regulations: Students learn about legal considerations and regulations specific to the hospitality and tourism industry.
These subjects equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to manage hospitality and tourism businesses, deliver exceptional guest experiences, and contribute to the growth and success of the industry. Graduates in Hospitality and Tourism Management are well-prepared for careers in hotel management, event planning, restaurant management, travel agencies, and tourism destination marketing.
Things to Think About When Choosing the Best Business Course
There are several crucial considerations to make before choosing a business course. The following are important points to bear in mind:
Personal Aspirations and Interests
Choose a course that is in line with your interests and professional goals. Consider the specific business areas that interest you and the abilities you hope to acquire.
Curriculum and Course Content
Do thoroughly analyze the course offerings and curriculum for your chosen program. Check the curriculum to see if it covers fundamental knowledge and advanced material in your desired fields. Look for courses that thoroughly understand the business while covering many pertinent topics.
Certification and Standing
Ensure the school offering the course is reputable and has accreditation for both. A program’s accreditation guarantees that it adheres to a set of quality standards and that both employers and other educational institutions will respect the degree you receive. Examine the school’s standing, the faculty’s qualifications, and their connections to the business world.
Networking and Industry Contacts
Think about the industry connections and networking opportunities made possible by the course. Look for programs that provide networking opportunities, guest lectures, internships, and cooperative education opportunities. These may offer beneficial connections and real-world business experience.
Career Opportunities
Consider the career opportunities offered by the course you are thinking about. Consider the potential salary range and the market demand for qualified professionals. Find out how often graduates successfully land jobs in pertinent fields and positions.
Specializations and Flexibility
Examine the course’s adaptability and whether it enables specialization in niche interests. Seek out programs with electives or concentrations that fit your career objectives. The ability to customize your education to fit your unique interests and career goals can be achieved by being flexible when selecting courses.
Resources and Assistance
Think about the tools and assistance the program offers its students. Access to libraries, research centers, computer labs, career services, and faculty advisors should all be available.
An encouraging learning environment can significantly improve your academic experience and offer helpful academic and professional development resources.
Alumni network and achievements
Research the institution’s and the course’s success stories and alumni network. Investigate the accomplishments and trajectories of graduates. A strong alumni network can offer beneficial mentorship, employment opportunities, and connections to the industry.
Price and Financial Assistance
Analyze the cost of the course, considering tuition, books, and other associated costs. Examine your financial situation and the various financial aid options, including student loans, grants, and scholarships. Verify that the course’s price is fair and fits into your spending plan.
Future Development and Trends
Keep up with the latest business trends and their potential for growth in the future. Consider how new technologies, globalization, sustainability, and industry-specific factors may affect your chosen path. Select a course that will help you get ready for the future and give you the skills you need for evolving business environments.
The Final Words
Choosing the best business courses requires considering various factors, including personal preferences, course content, accreditation, networking opportunities, networking skills, flexibility, resources, cost, future trends, and alumni success. A business degree offers the expertise and knowledge required for success in various business fields. It is crucial to pick courses covering new trends and providing access to resources and networking opportunities. Choosing coursework that aligns with one’s interests and professional objectives ensures a fulfilling educational experience and lays the groundwork for professional development in the fast-paced business world. We hope that this article helped in providing the best courses to study for business. Let us know in the comments, we are looking forward to reading them.